Physicists at the ITMO University in Russia and the Australian National University have developed the first controlled nano-diamond light source. Experiments have shown that the diamond casing can double the emission rate of the light source and can be controlled without any additional nano and microstructure. This result is achieved by defects in the diamond lattice. The research results have important significance for the development of quantum computers and optical networks.
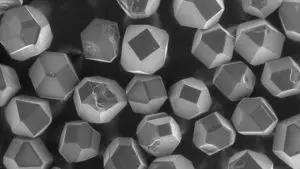
One of the key areas of modern nanophotonics is the design of active dielectric nano-antennas or controlled photon sources. As the basis of nano-antennas, scientists typically use plasma metal nanoparticles. However, the optical loss and heating of these particles prompted scientists to look for alternatives. Recently, members of the International Laboratory of Nanophotonics and Metamaterials at ITMO University have developed a new concept for new active dielectric nano-antennas based on nanodiamonds.
Nanodiamonds are carbon nanostructures with unique properties. They have a sufficiently high refractive index, high thermal conductivity and low interaction activity. The scientists used nano-diamonds called the so-called nitrogen vacancy center (NV-center). These are artificially produced by removing carbon atoms from the diamond lattice. The open vacancies are then connected to the implanted nitrogen atoms. The electron spins of these NV centers are easily controlled by light, and electron spins can be used to record quantum information.
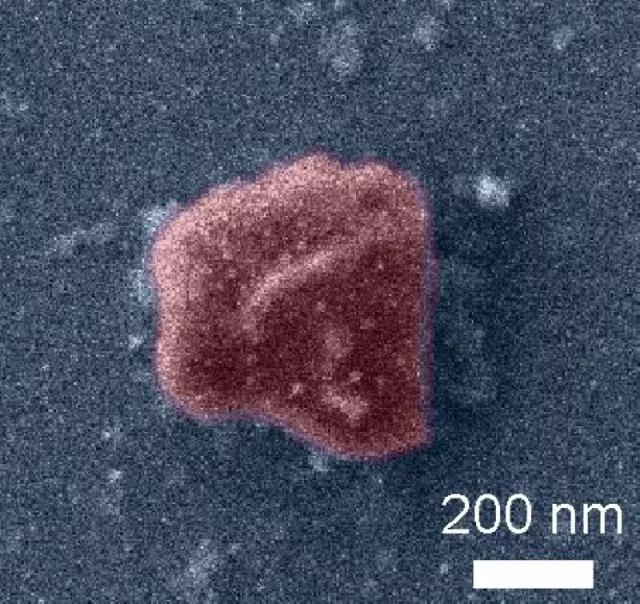
Scientists at ITMO University studied the optical properties of nanodiamonds and found that their radiation can be enhanced by combining the NV central luminescence spectrum with the optical Mie resonance of diamond nanoparticles. This can be achieved at a specific location in the center of the NV and at a suitable particle size. This can increase the Purcell factor of nanodiamonds. This indicator is used to estimate how the diamond casing affects the rate at which the source spontaneously emits radiation. If the Purcell factor increases, the fluorescence decay time decreases, and the signal itself becomes stronger and easier to read.
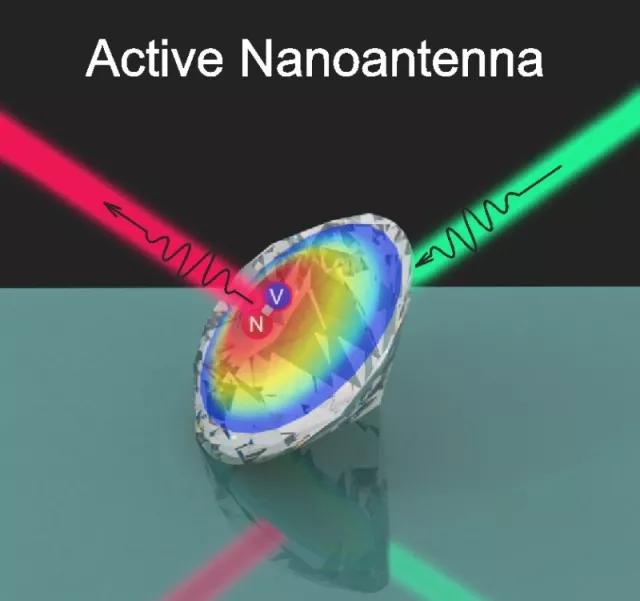
The researchers emphasized that this effect is achieved by using the properties of nanodiamonds. “Usually, in order to accelerate the radiation, one has to build a complex resonator system, but we managed to achieve similar results without any additional structure. We have experimentally proved that using simple physical methods can accelerate at least twice the luminescence attenuation. "Dmitry Zuev of the International Nanophotonics and Metamaterials Laboratory," said Dmitry Zuev.
In fact, although the researchers developed a theoretical model for the behavior of a single photon source in a diamond shell, experiments were performed on nanodiamonds with multiple NV centers. Calculations show that the illuminating speed can be increased by several tens of times.
Diamond is one of the special materials in nature, with the highest hardness, low friction coefficient, high elastic modulus, high thermal conductivity, high insulation, wide energy gap, high acoustic propagation rate and good chemical stability, as shown in the following table. Although natural diamonds have these unique properties, they have always existed only in the form of gemstones, and their versatility and rarity greatly limit their applications. The CVD diamond film prepared by Luoyang Yuxin Diamond combines these excellent physical and chemical properties, and the cost is lower than that of natural diamond. It can prepare various geometric shapes and has broad application prospects in the fields of electronics, optics and machinery.
Ground Screw For Park And City Building
Using Honde Ground Screws requires no excavation or concrete pouring and leaves the landscape and vegetation untouched. They are easy to dismantle and relocate for temporary projects.
Solar lighting
Bollard lighting
Awnings and sunsails
Playground equipment
Walking trail lighting
Paintball courses and fences
Goal posts and field equipment
Park and sports field lighting
Park and event structures
Screw in Ground Anchors,Building Deck with Ground Screws,Ground Anchors for Retaining Walls
Hebei Honde Plastic & Metal Co., Ltd. , https://www.foundation-system.com