- The mechanism of cleavage cleavage is not fully understood. It can be considered that there may be some high tensile stress regions in martensite due to quenching and phase transformation stress, and even microcracks may exist. Further, the e-carbide which is precipitated in the direction, the middle ridge of the twinned martensite, and the like are easily cracked and become a crack source when subjected to an external force. As shown in Figure 5-4 (a). As the stress increases, the small cracks expand in a stepwise manner in the quasi-cleavage plane to form a river pattern Figure 5-4(b). Due to the existence of a large number of dislocations and defects in the martensite, the lattice is severely distorted, and the spatial orientation between the martensite sheets in the same grain is somewhat different; it is difficult to crack the inside of the grain. When the crack propagates inside the severely distorted grains of the lattice, large plastic deformation occurs at the boundary adjacent to each other to form a tearing manner, forming a tearing rib, or forming a microporous polymerized dimple, sometimes forming a toughness. The litter belt is shown in Figure 5-4(c).
In the fracture of mechanical parts, quasi-cleavage fractures are often encountered, but more are mixed fractures of quasi-cleavage and other fractures.
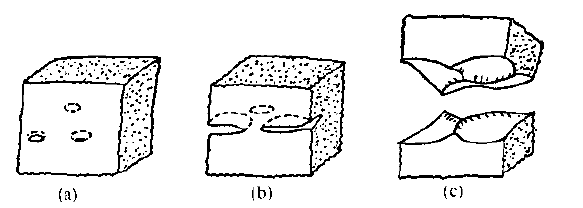 Figure 5-4 Schematic diagram of quasi-cleavage crack formation mechanism(a) initiation of quasi-cleavage cracks; (b) expansion of quasi-cleavage cracks; (c) joining by tearing to form tearing edges
Figure 5-4 Schematic diagram of quasi-cleavage crack formation mechanism(a) initiation of quasi-cleavage cracks; (b) expansion of quasi-cleavage cracks; (c) joining by tearing to form tearing edgesSome material quasi-cleavage fractures are given below.
 Figure 5-5 HZ120F impact fracture quasi-clearing - secondary crack × 800
Figure 5-5 HZ120F impact fracture quasi-clearing - secondary crack × 800
Figure 5-6 45# quasi-cleavage (visible to the river pattern) × 100
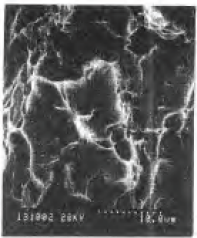
Figure 5-7 Quasi-cleavage fracture of Al-Li alloy × 500
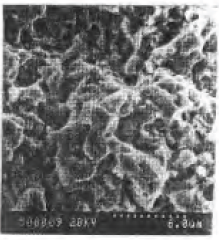
Figure 5-8 W6Mo5Cr4V2 1230 °C quenching cryogenic treatment +550 tempering

Figure 5-9 Ti3AL 960 ° C solution treatment quasi-cleavage fracture
Single Sphere Type
Hot Water, Oil, Acid, Alkali.
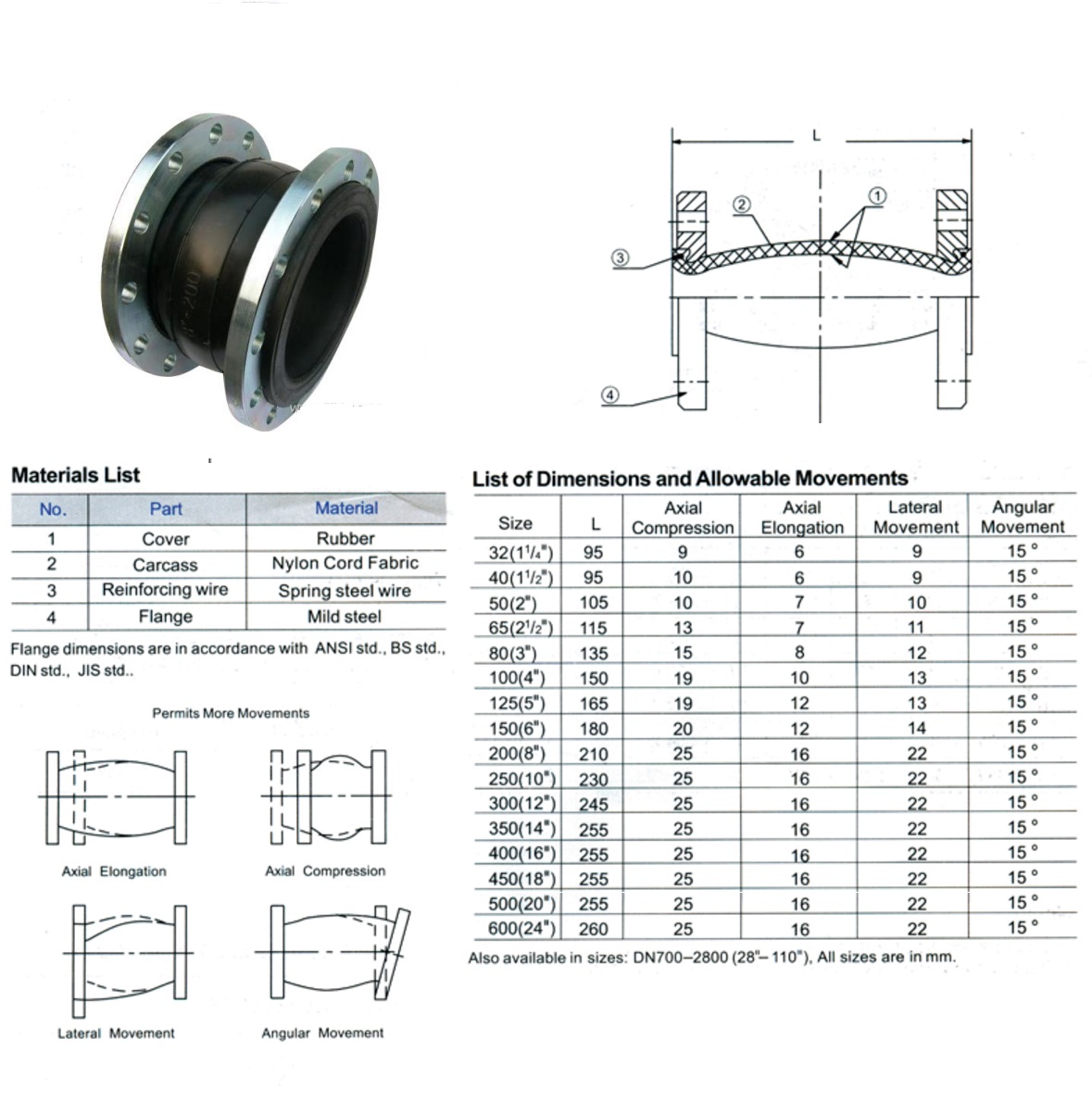
Double Sphere Type
Operating Conditions :
Operating Pressure:PN10/PN16
Explosive Pressure:3.0/4.5Mpa
Vacuum Rating:400/650/750 mmHg
Temperature :
EPDM:-10℃ to 120 ℃
NBR:-10℃ to 82℃
Neoprene:-10℃ to 110℃
Medium :
Air, Water, Sea Water,
Hot Water, Oil, Acid, Alkali.
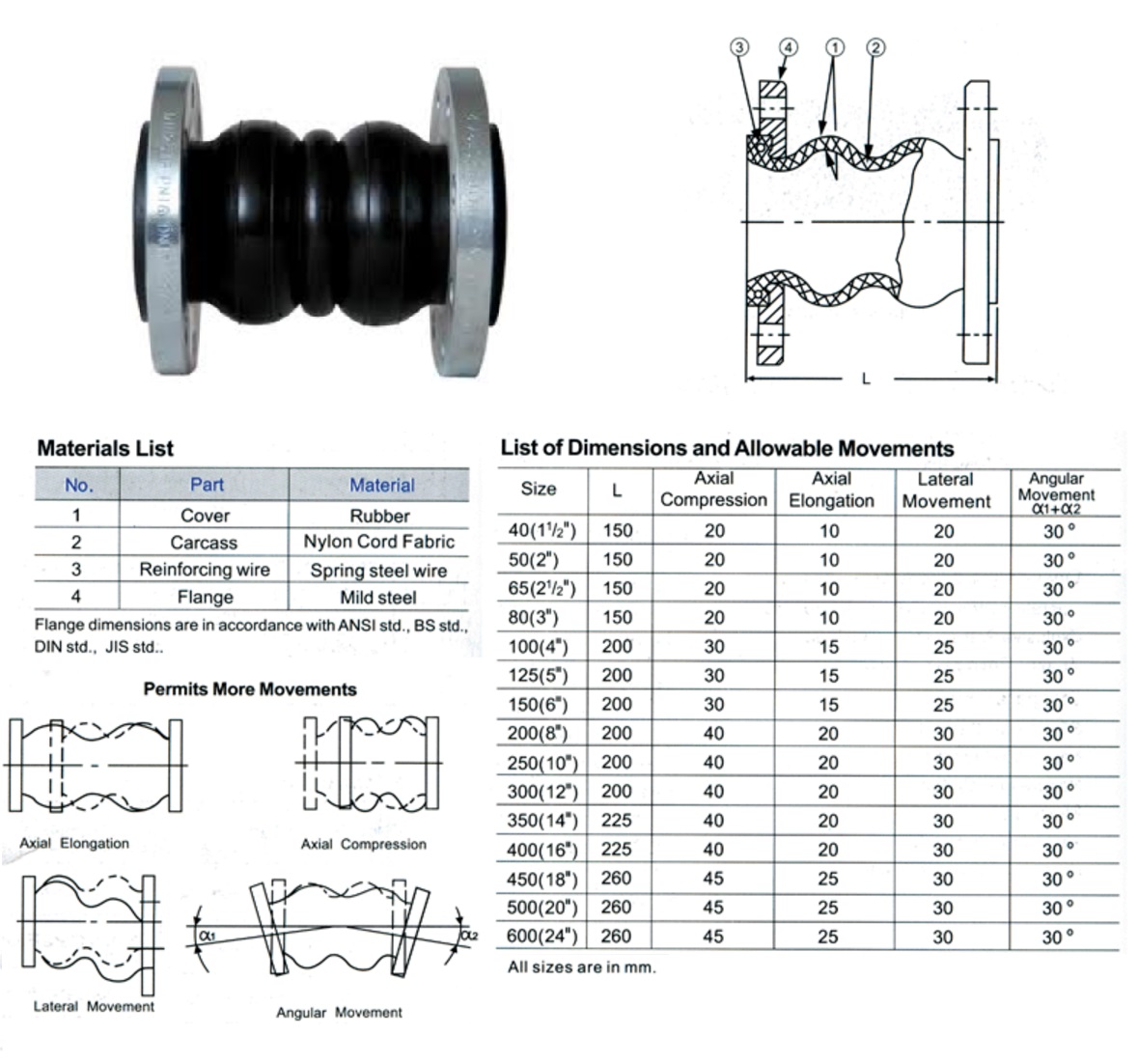
Flange Type Rubber Expansion Joint
Flange Type Rubber Expansion Joint,Flange Rubber Joint,Flange Expansion Joint,Flange Rubber Bridge Expansion Joint
HEBEI ZIFENG NEW ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD. , https://www.zifengpipeline.com