The single-layer electroplated CBN grinding wheel has excellent grinding performance and is suitable for forming and high-speed grinding. However, the grinding wheel should not be directly rectified, and the manufacturing accuracy of the grinding wheel has become an important factor affecting the final machining accuracy. The external grinding wheel has a simple manufacturing process and low cost, but the exposed cutting edge is uneven, the initial grinding surface accuracy is difficult to improve, and the grinding wheel has a low durability and serious abrasive loss. This is commonly used in the domestic and foreign electroplating CBN grinding wheels. problem. First, the separate structure of the grinding wheel The grinding wheel shown in Figure 1 is divided into four parts: the grinding wheel bearing body with a tapered hole; the elastic thin-walled sleeve; the non-abrasive plating metal layer combined with the thin-walled sleeve; and the grinding wheel Granular plating metal layer. The taper hole design is to meet the coaxial requirements when assembling with the grinding wheel shaft. Second, the electroplating process Electroplating process is mainly divided into matrix and abrasive preparation, plating solution preparation, sand planting and electroplating (pre-plating, thick plating), etc., as well as for the medium-term treatment of abrasive and other high-improvement and related plating Treatment process. The plating solution was prepared by using Watts nickel as a solution containing cobalt ions, as shown in Table 1. Table 1 Plating solution preparation Bath composition (g/L) Operating conditions NiSo4·7H2O 200-220
H3BO3 30-40
CoSO4·7H2O 25-35
NaCl 10-20
Sodium dodecyl sulfate 0.1 PH 4.0-4.5
Temperature: 45-60°C
Current density: 1-4A/dm2
Stirring: According to the process, the relevant problems to be noticed in the electroplating process: The strict pre-treatment process must be adopted on the surface of the grinding wheel base; The CBN grinding particles must be strictly screened to reduce the size difference distribution of the particles; The chemical treatment process is used to effectively remove Abrasive surface stains, improve the wetting ability of the abrasive; The sharp corner of the grinding wheel adopts large-arc smooth joint to optimize the current distribution in the edge area; The local discontinuous sand-up device makes full use of the “scattered pole†to change the current density distribution to cause local Stabilizing the sand area can reduce the sanding time by 1/3-1/2, and it can well ensure the uniformity of the deposit during the sand planting; the plating parameters in the early stage of thick plating should be properly reduced; the post-plating treatment process can be greatly reduced Small hydrogen embrittlement tends to increase plating adhesion by more than 4 times.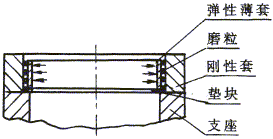
Fig. 2 Acquired height of the coated abrasive grain Third, medium-intermediate treatment of equal height is carried out after preplating sand-planting. Figure 2 shows the expansion of an elastic thin sleeve using externally coated abrasive particles and the internal compression of a standard rigid sleeve, so that the post-plating cutting edge changes the height distribution of the cutting edge with reference to the inner surface of the standard rigid sleeve. The elastic thin sleeve can slide freely along the bottom surface of the pad. Thin sleeve expansion is achieved using a uniform extrusion effect of a specially prepared plug through a central through hole. Suppose that: the effective diameter of the plug is D; the inner diameter of the elastic thin shell is d1; the outer diameter is d2; the thickness of the half of the pre-plating is Dr3; the average particle size of the abrasive is d3 (the maximum value is d3max, the minimum value is d3min); the inner diameter of the rigid sleeve is D4; The inner diameter of the pad is d5; the thickness of the fixed sand half is Dr6. The minimum protrusion height of abrasive grains is d (based on pre-plating). The operating process design conditions are: d4/21/D[Dr3+(d2-d1)/2]+D/2+d3min4/2+(d3min-d); d2+2Dr3+2d3max4; d1D52 40%d3
H3BO3 30-40
CoSO4·7H2O 25-35
NaCl 10-20
Sodium dodecyl sulfate 0.1 PH 4.0-4.5
Temperature: 45-60°C
Current density: 1-4A/dm2
Stirring: According to the process, the relevant problems to be noticed in the electroplating process: The strict pre-treatment process must be adopted on the surface of the grinding wheel base; The CBN grinding particles must be strictly screened to reduce the size difference distribution of the particles; The chemical treatment process is used to effectively remove Abrasive surface stains, improve the wetting ability of the abrasive; The sharp corner of the grinding wheel adopts large-arc smooth joint to optimize the current distribution in the edge area; The local discontinuous sand-up device makes full use of the “scattered pole†to change the current density distribution to cause local Stabilizing the sand area can reduce the sanding time by 1/3-1/2, and it can well ensure the uniformity of the deposit during the sand planting; the plating parameters in the early stage of thick plating should be properly reduced; the post-plating treatment process can be greatly reduced Small hydrogen embrittlement tends to increase plating adhesion by more than 4 times.

Fig. 2 Acquired height of the coated abrasive grain Third, medium-intermediate treatment of equal height is carried out after preplating sand-planting. Figure 2 shows the expansion of an elastic thin sleeve using externally coated abrasive particles and the internal compression of a standard rigid sleeve, so that the post-plating cutting edge changes the height distribution of the cutting edge with reference to the inner surface of the standard rigid sleeve. The elastic thin sleeve can slide freely along the bottom surface of the pad. Thin sleeve expansion is achieved using a uniform extrusion effect of a specially prepared plug through a central through hole. Suppose that: the effective diameter of the plug is D; the inner diameter of the elastic thin shell is d1; the outer diameter is d2; the thickness of the half of the pre-plating is Dr3; the average particle size of the abrasive is d3 (the maximum value is d3max, the minimum value is d3min); the inner diameter of the rigid sleeve is D4; The inner diameter of the pad is d5; the thickness of the fixed sand half is Dr6. The minimum protrusion height of abrasive grains is d (based on pre-plating). The operating process design conditions are: d4/21/D[Dr3+(d2-d1)/2]+D/2+d3min4/2+(d3min-d); d2+2Dr3+2d3max4; d1D52 40%d3